Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is often referred to as “adult onset” or “insulin non-dependent” diabetes. With type 2 diabetes, the pancreas can still make insulin, but either it doesn’t make enough, or the body’s cells don’t respond to it as effectively as they used to. When the cells don’t respond as effectively, this is called “insulin resistance.” This means glucose is not getting into the cells where it’s needed to function properly.
Type 2 diabetes often runs in families, but the following risk factors can also increase a person’s chances of developing it:
- Overweight
- Poor diet
- Inactivity/lack of exercise
- Family history of diabetes
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Age 45 years or older
- Race or ethnicity (Blacks, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans have higher rates of type 2 diabetes)
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
Symptoms can include:
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Skin darkening in areas such as in armpits and the neck
- Frequent urination
- Frequent infections
- Slow-healing sores
- Blurry vision
- Pain or tingling in hands and feet
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes
To determine whether someone has type 2 diabetes, doctors may use one or more of these tests:
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test: This measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to red blood cells, or hemoglobin over the last six to 12 weeks. Since a red blood cell can live about 12 weeks, this test shows the average over that time. An A1C of 6.5 percent or higher indicates diabetes. This test is often performed twice to make sure it’s accurate.
| A1C Test Results | |
|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 5.7% |
| Pre-diabetes | 5.7% to 6.4% |
| Diabetes | 6.5% or higher |
Random blood sugar test: A blood sample is taken at a random time and measures the amount of glucose, or sugar, present in the blood at that moment. If the sugar level is 200 milligrams or more per decimeter (mg/dL) or 11.1 (or 11.1 mmol/L), it may indicate diabetes.
Oral glucose tolerance test: This involves drinking a sugary beverage after fasting and then testing the blood several times for up to two hours to determine how the body is responding to the sugar intake.
Fasting blood sugar test: A blood sample is taken after an overnight fast. It measures the level of sugar in the blood. A glucose level of less than 100 milligrams or more per decimeter (mg/dL) is normal. Levels 101 to 125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL and over in two separate tests indicates diabetes.
Diabetes autoantibody tests: These blood tests determine whether a person has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. It looks for antibodies, or special proteins, that attack viruses or other foreign substances found in the blood. People with type 1 diabetes have these antibodies, but those with type 2 do not.
Managing type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes can be managed or sometimes even reversed by making lifestyle changes that include:
- Losing weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can have a big impact on type 2 diabetes.
- Eating healthy foods: Eating more fruits and vegetables can reduce type 2 diabetes risk by 50 percent.2
- Exercising regularly: Getting physical exercise for up to 150 minutes per week can improve blood glucose levels, aid in weight loss, and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.3
In addition to lifestyle changes, some people with type 2 diabetes must manage their condition in these ways:
-
Blood sugar testing: They may need to test their blood sugar levels throughout the day. There are a few ways to do this:
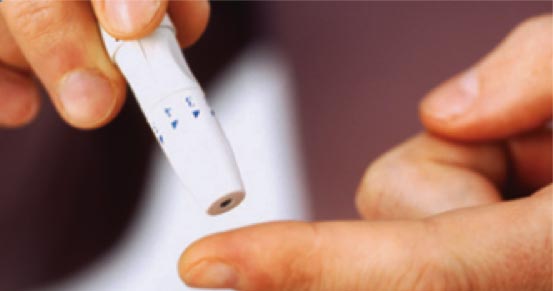
- Fingerstick checks: This uses a small sharp needle to poke the finger to draw blood, which is then placed on a glucose test strip and fed into a meter that provides a blood sugar level reading.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGM): These devices use a sensor placed under the skin to measure blood sugars every few minutes. They are often used in combination with insulin pumps for insulin therapy.
- Medication: Sometimes doctors prescribe oral medications to help patients control their blood sugar.
-
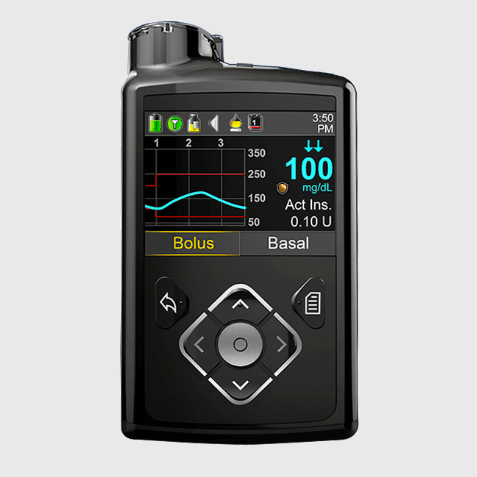
Insulin therapy: Some people need insulin therapy to control their blood sugar levels. Often this begins with a long-acting insulin injection at night, but sometimes it will require more frequent insulin injections during the day. This is why some people may choose to use the following insulin-delivery methods:

- Insulin pen: This device looks like an ink pen but has an insulin cartridge and a very fine needle at the end to inject insulin as needed throughout the day.
- Insulin pump: This is a device worn outside the body. It is programmed to deliver certain amounts of insulin through a small tube with a tiny needle at the end that goes under the skin. When a pump is used with CGM, it reduces the amount of fingerstick checks throughout the day to test insulin.
- Ongoing care: People with type 2 diabetes will likely have to take an A1C test several times a year, so their doctor can see how well they are managing their blood sugar levels.
What can happen if type 2 diabetes goes untreated?
Diabetes affects many of the body’s systems. If it isn’t managed properly, it can lead to severe complications, some of which could lead to death. Complications include:
- Nerve damage
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Blood circulation issues
- Kidney damage
- Eye damage and potential blindness
This is why it’s important that people with type 2 diabetes work with their healthcare team to ensure they are effectively managing their diabetes. Managing diabetes is ongoing and can be challenging. If you need support, remember Medtronic is here to help wherever you are along your journey.
Looking for more tips? Join the list
Subscribe to our newsletter, News to Infuse and receive monthly diabetes tips and helpful information.
1. National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/diabetes-stat-report.html. Published February 11, 2020. Accessed January 12, 2021.
2. Zheng J-S, Sharp SJ, Imamura F, et al. Association of plasma biomarkers of fruit and vegetable intake with incident type 2 diabetes: EPIC-InterAct case-cohort study in eight European countries. https://www.bmj.com/content/370/bmj.m2194.abstract. Published July 8, 2020. Accessed January 12, 2021.
3. Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Fernhall B, et al. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Diabetes Association: joint position statement. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(12):e147-e167. doi:10.2337/dc10-9990.
4. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes with Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;346(6):393-403. doi:10.1056/nejmoa012512.