What is hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is what happens when there is too much sugar in the blood. For people living with diabetes, the body either has too little insulin, or loses the ability to process insulin properly. This often results in hyperglycemia, also known as high blood glucose (BG) or high blood sugar.
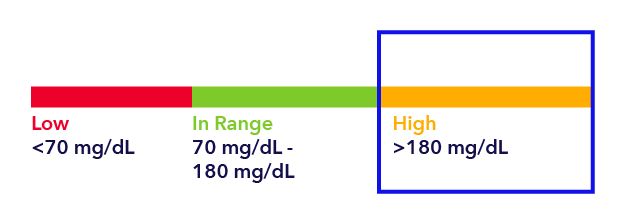
A major goal of managing diabetes is to avoid high BGs as much as possible and to properly treat hyperglycemia as soon as it is noticed. Hyperglycemia can cause serious complications when left untreated. For people living with diabetes, blood sugar is considered "high" when it rises above 180 mg/dL. High blood sugars are most common after meals and can be dangerous if untreated.
Causes of hyperglycemia
Glucose levels can rise too high for many reasons. Here are just a few1:





Most hyperglycemia occurs when there is some insulin in the body, but not enough to keep glucose levels within your target range.
- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar) Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9815-hyperglycemia-high-blood-sugar. Accessed 23MAY2024.

What are the symptoms of hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia symptoms can appear when glucose levels are elevated. Symptoms will typically develop over the course of days or weeks, and can include1,2:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
- High blood sugar
- Headache
- High levels of sugar in the urine
- Fatigue
Be aware of what these symptoms look and feel like. For example, increased thirst is when you drink plenty of water, but it still doesn’t feels like enough. Another example is high levels of sugar in your urine; you may notice your urine is cloudy and smells sweet. Early recognition of symptoms and consistently checking your blood sugar are important actions for treating hyperglycemia.







- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Glucose) The American Diabetes Association Page. https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/blood-glucose-testing-and-control/hyperglycemia. Accessed 3AUG2021.
- Hyperglycemia in diabetes. The Mayo Clinic Page. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hyperglycemia/symptoms-causes/syc-20373631. Accessed 3 AUG2021
How to treat hyperglycemia
When hyperglycemia occurs, you should take insulin to lower your blood sugar. Other effective ways of lowering blood sugar include exercise and making necessary changes to your diet.
If your blood sugar is elevated above 240 mg/dL, you should check your urine for ketones, as exercising with ketones in your system can further elevate your blood sugar.
Your doctor may also propose changes to your medication or insulin as a means of treating hyperglycemia.

Risks and complications
Left untreated, hyperglycemia can pose serious health risks. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a major complication that can result from hyperglycemia.
As this condition can cause your body to create a surplus of ketones, you may be unable to release them effectively, leading to ketoacidosis. You should seek immediate treatment if you experience any of these symptoms:
- Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- Confusion
- Feeling tired, sluggish, or weak
- Flushed, hot, dry skin
- Rapid, deep breathing and shortness of breath
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Fruity scented breath
- Unconsciousness
Prevention tips
- Adhering to your diabetes treatment plan and monitoring your blood sugar are important daily steps to take.
- An insulin pump can automatically deliver insulin to bring sugar levels within an acceptable range.
- A healthy diet plan and timing your meals can help to avoid hyperglycemia, particularly if you take insulin or medication.
- Exercise can also lower your blood sugar levels – consult with your doctor to see if a more active lifestyle could benefit you.

Looking for more tips? Join the list
Subscribe to our newsletter, News to Infuse, and receive monthly diabetes tips and helpful information.
Footnotes
‡ Refers to SmartGuard™ feature. Individual results may vary.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Medtronic Diabetes insulin infusion pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems and associated components are limited to sale by or on the order of a physician and should only be used under the direction of a healthcare professional familiar with the risks associated with the use of these systems. - Successful operation of the insulin infusion pumps and/or continuous glucose monitoring systems requires adequate vision and hearing to recognize alerts and alarms.
Medtronic Diabetes Insulin Infusion Pumps
Insulin pump therapy is not recommended for individuals who are unable or unwilling to perform a minimum of four blood glucose tests per day. - Insulin pumps use rapid-acting insulin. If your insulin delivery is interrupted for any reason, you must be prepared to replace the missed insulin immediately.